Prerequisites #
Update the AlmaLinux System #
Any installation process should ideally be preceded by updating your system. An updated system minimizes the possibility of encountering conflicts caused by outdated packages during the installation.
sudo dnf upgrade --refresh
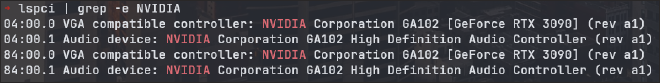
Check if system can see NVIDIA GPU #
lspci | grep -e NVIDIA
An output might look like this:
Check the Secure Boot Status #
Checking the secure boot status is a crucial step. If secure boot is enabled on your system, you might experience difficulties during the Nvidia driver installation. In such scenarios, you may need to turn off the secure boot or undertake additional measures to circumvent conflicts.
mokutil --sb-state
Tips: disabling secure boot can help big time if you struggle installing NVIDIA driver
Disabling Nouveau Drivers #
Conflicts may arise between Nouveau and Nvidia drivers. Therefore, you should prevent these conflicts by blacklisting Nouveau drivers
echo "blacklist nouveau" | sudo tee /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist-nouveau.conf
echo 'omit_drivers+=" nouveau "' | sudo tee /etc/dracut.conf.d/blacklist-nouveau.conf
Then regenerate all Dracut initramfs images and update the module dependency list
sudo dracut --regenerate-all --force
sudo depmod -a
Add EPEL Repo #
Activating and incorporating an additional repository of software packages into AlmaLinux. This process expands the range of software you can install while ensuring compatibility with your specific version of AlmaLinux, such as the case with installing the NVIDIA Drivers packages.
sudo dnf install \
https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-8.noarch.rpm \
https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-next-release-latest-8.noarch.rpm
Installing NVDIA driver #
Adding NVIDIA Repo RPM for AlmaLinux 8 #
sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo http://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/rhel8/$(uname -i)/cuda-rhel8.repo
Installing the required dependencies #
sudo dnf install kernel-headers-$(uname -r) kernel-devel-$(uname -r) tar bzip2 make automake gcc gcc-c++ pciutils elfutils-libelf-devel libglvnd-opengl libglvnd-glx libglvnd-devel acpid pkgconfig dkms
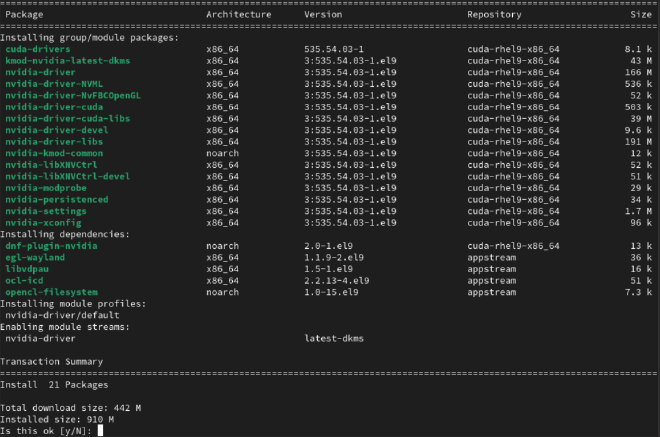
Installing NVIDIA driver module #
sudo dnf module install nvidia-driver:latest-dkms
Reboot #
sudo reboot
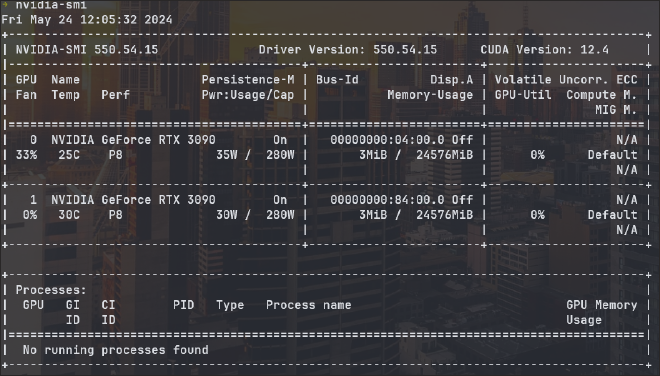
Verifying the NVIDIA drivers installation #
nvidia-smi
Undervolt GPU #
My server has 2x1100W PSU (1 redundant). While others say that it’s fine with 2x 3090, I also went ahead and undervolt the 3090 to 280w limit by creating a new systemd service to set power limit on startup.
Create a file called “nvidia-undervolt.service” at /etc/systemd/system/
[Unit]
Description=Set NVIDIA power limit below default
After=nvidia-persistenced.service
[Service]
Type=oneshot
User=root
ExecStart=/usr/bin/nvidia-smi -i 00000000:0C:00.0 -pl 280
ExecStart=/usr/bin/nvidia-smi -i 00000000:0D:00.0 -pl 280
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
and create a timer file “nvidia-undervolt.timer” at the same dir
[Unit]
Description=Set power limit 5 seconds after boot
[Timer]
OnBootSec=5
[Install]
WantedBy=timers.target
Note that NVIDA Persistence daemon is located at /usr/lib/systemd/system/nvidia-persistenced.service
Uninstall NVIDIA driver #
If you need to remove the Nvidia drivers for any reason, you can do so with:
sudo dnf remove -y nvidia-driver
sudo dnf module reset -y nvidia-driver